Abstract
Purpose
Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) is an inflammatory mediator produced by neutrophils, macrophages, myeloid dendritic and endothelial cells. During sepsis a massive inflammatory activation and coagulation/fibrinolysis dysfunction occur. PTX3, as a mediator of inflammation, may represent an early marker of severity and outcome in sepsis.
Methods
This study is based on a prospective trial regarding the impact of glycemic control on coagulation in sepsis. Ninety patients admitted to three general intensive care units were enrolled when severe sepsis or septic shock was diagnosed. At enrollment, we recorded sepsis signs, disease severity, coagulation activation [prothrombin fragments 1 + 2 (F1+2)] and fibrinolysis inhibition [plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1)]. We measured plasma PTX3 levels at enrollment, everyday until day 7, then at days 9, 11, 13, 18, 23 and 28. Mortality was recorded at day 90.
Results
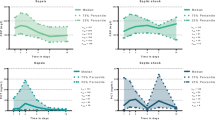
Although not different on day 1, PTX3 remained significantly higher in non-survivors than in survivors over the first 5 days (p = 0.002 by general linear model). On day 1, PTX3 levels were higher in septic shock than in severely septic patients (p = 0.029). Day 1 PTX3 was significantly correlated with platelet count (p < 0.001), SAPS II score (p = 0.006) and SOFA score (p < 0.001). Day 1 PTX3 was correlated with F1+2 concentration and with PAI-1 activity and concentration (p < 0.05 for all).
Conclusions
Persisting high levels of circulating PTX3 over the first days from sepsis onset may be associated with mortality. PTX3 correlates with severity of sepsis and with sepsis-associated coagulation/fibrinolysis dysfunction.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottazzi B, Garlanda C, Cotena A, Moalli F, Jaillon S, Deban L, Mantovani A (2009) The long pentraxin PTX3 as a prototypic humoral pattern recognition receptor: interplay with cellular innate immunity. Immunol Rev 227:9–18
Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM (2003) C-reactive protein: a critical update. J Clin Invest 111:1805–1812
Vidal Alles V, Bottazzi B, Peri G, Golay J, Introna M, Mantovani A (1994) Inducible expression of PTX3, a new member of the pentraxin family, in human mononuclear phagocytes. Blood 84:3483–3493
Doni A, Mantovani G, Porta C, Tuckermann J, Reichardt HM, Kleiman A, Sironi M, Rubino L, Pasqualini F, Nebuloni M, Signorini S, Peri G, Sica A, Beck-Peccoz P, Bottazzi B, Mantovani A (2008) Cell-specific regulation of PTX3 by glucocorticoid hormones in hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem 283:29983–29992
Garlanda C, Bottazzi B, Bastone A, Mantovani A (2005) Pentraxins at the crossroads between innate immunity, inflammation, matrix deposition, and female fertility. Annu Rev Immunol 23:337–366
Napoleone E, di Santo A, Bastone A, Peri G, Mantovani A, de Gaetano G, Donati MB, Lorenzet R (2002) Long pentraxin PTX3 upregulates tissue factor expression in human endothelial cells: a novel link between vascular inflammation and clotting activation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:782–787
Napoleone E, di Santo A, Peri G, Mantovani A, de Gaetano G, Donati MB, Lorenzet R (2004) The long pentraxin PTX3 up-regulates tissue factor in activated monocytes: another link between inflammation and clotting activation. J Leukoc Biol 76:203–209
He X, Han B, Bai X, Zhang Y, Cypel M, Mura M, Keshavjee S, Liu M (2010) PTX3 as a potential biomarker of acute lung injury: supporting evidence from animal experimentation. Intensive Care Med 36:356–364
Cinel I, Opal SM (2009) Molecular biology of inflammation and sepsis: a primer. Crit Care Med 37:291–304
Abraham E, Singer M (2007) Mechanisms of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 35:2408–2416
Novack V, Eisinger M, Frenkel A, Terblanche M, Adhikari NK, Douvdevani A, Amichay D, Almog Y (2009) The effects of statin therapy on inflammatory cytokines in patients with bacterial infections: a randomized double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial. Intensive Care Med 35:1255–1260
Mauri T, Coppadoro A, Bellani G, Bombino M, Patroniti N, Peri G, Mantovani A, Pesenti A (2008) Pentraxin 3 in acute respiratory distress syndrome: an early marker of severity. Crit Care Med 36:2302–2308
Sprong T, Peri G, Neeleman C, Mantovani A, Signorini S, van der Meer JW, van Deuren M (2009) Pentraxin 3 and C-reactive protein in severe meningococcal disease. Shock 31:28–32
Latini R, Maggioni AP, Peri G, Gonzini L, Lucci D, Mocarelli P, Vago L, Pasqualini F, Signorini S, Soldateschi D, Tarli L, Schweiger C, Fresco C, Cecere R, Tognoni G, Mantovani A, Lipid Assessment Trial Italian Network (LATIN) Investigators (2004) Prognostic significance of the long pentraxin PTX3 in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 110:2349–2354
Inoue K, Sugiyama A, Reid PC, Ito Y, Miyauchi K, Mukai S, Sagara M, Miyamoto K, Satoh H, Kohno I, Kurata T, Ota H, Mantovani A, Hamakubo T, Daida H, Kodama T (2007) Establishment of a high sensitivity plasma assay for human pentraxin3 as a marker for unstable angina pectoris. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:161–167
Yilmaz MI, Axelsson J, Sonmez A, Carrero JJ, Saglam M, Eyileten T, Caglar K, Kirkpantur A, Celik T, Oguz Y, Vural A, Yenicesu M, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P (2009) Effect of renin angiotensin system blockade on Pentraxin 3 levels in type-2 diabetic patients with proteinuria. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:535–541
Muller B, Peri G, Doni A, Torri V, Landmann R, Bottazzi B, Mantovani A (2001) Circulating levels of the long pentraxin PTX3 correlate with severity of infection in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 29:1404–1407
Savioli M, Cugno M, Polli F, Taccone P, Bellani G, Spanu P, Pesenti A, Iapichino G, Gattinoni L (2009) Tight glycemic control may favor fibrinolysis in patients with sepsis. Crit Care Med 37:424–431
American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference (1992) Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med 20:864–874
van den Berghe G, Wouters P, Weekers F, Verwaest C, Bruyninckx F, Schetz M, Vlasselaers D, Ferdinande P, Lauwers P, Bouillon R (2001) Intensive insulin therapy in the critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 345:1359–1367
Ohno-Machado L, Resnic FS, Matheny ME (2006) Prognosis in critical care. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:567–599
Vincent JL (2006) Organ dysfunction in patients with severe sepsis. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 7(S2):S69–S72
Mauri T, Pivi S, Bigatello LM (2008) Prolonged mechanical ventilation after critical illness. Minerva Anestesiol 74:297–301
Ware LB, Matthay MA (2000) The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Eng J Med 342:1334–1349
Ware LB, Matthay MA, Parsons PE, Thompson BT, Januzzi JL, Eisner MD, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Clinical Trials Network (2007) Pathogenic and prognostic significance of altered coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med 35:1821–1828
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut JF, Gerlach H, Harvey M, Marini JJ, Marshall J, Ranieri M, Ramsay G, Sevransky J, Thompson BT, Townsend S, Vender JS, Zimmerman JL, Vincent JL (2008) Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Intensive Care Med 34:17–60. Erratum in (2008) Intensive Care Med 34:783–785
Reading PC, Bozza S, Gilbertson B, Tate M, Moretti S, Job ER, Crouch EC, Brooks AG, Brown LE, Bottazzi B, Romani L, Mantovani A (2008) Antiviral activity of the long chain pentraxin PTX3 against influenza viruses. J Immunol 180:3391–3398
Deban L, Jarva H, Lehtinen MJ, Bottazzi B, Bastone A, Doni A, Jokiranta TS, Mantovani A, Meri S (2008) Binding of the long pentraxin PTX3 to factor H: interacting domains and function in the regulation of complement activation. J Immunol 181:8433–8440
Soares AC, Souza DG, Pinho V, Vieira AT, Nicoli JR, Cunha FQ, Mantovani A, Reis LF, Dias AA, Teixeira MM (2008) Dual function of the long pentraxin PTX3 in resistance against pulmonary infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae in transgenic mice. Microbes Infect 8:1321–1329
Jaillon S, Peri G, Delneste Y, Frémaux I, Doni A, Moalli F, Garlanda C, Romani L, Gascan H, Bellocchio S, Bozza S, Cassatella MA, Jeannin P, Mantovani A (2007) The humoral pattern recognition receptor PTX3 is stored in neutrophil granules and localizes in extracellular traps. J Exp Med 204:793–804
Gaziano R, Bozza S, Bellocchio S, Perruccio K, Montagnoli C, Pitzurra L, Salvatori G, De Santis R, Carminati P, Mantovani A, Romani L (2004) Anti-Aspergillus fumigatus efficacy of pentraxin 3 alone and in combination with antifungals. Antimicrob Agents Chemoter 48:4414–4421
Salio M, Chimenti S, De Angelis N, Molla F, Maina V, Nebuloni M, Pasqualini F, Latini R, Garlanda C, Mantovani A (2008) Cardioprotective function of the long pentraxin PTX3 in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 117:1055–1064
Marik PE, Raghavan M (2004) Stress-hyperglycemia, insulin and immunomodulation in sepsis. Intensive Care Med 30:748–756
He X, Han B, Liu M (2007) Long pentraxin 3 in pulmonary infection and acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292:L1039–L1049
Souza DG, Amaral FA, Fagundes CT, Coelho FM, Arantes RM, Sousa LP, Matzuk MM, Garlanda C, Mantovani A, Dias AA, Teixeira MM (2009) The long pentraxin PTX3 is crucial for tissue inflammation after intestinal ischemia and reperfusion in mice. Am J Pathol 174:1309–1318
Okutani D, Han B, Mura M, Waddell TK, Keshavjee S, Liu M (2007) High-volume ventilation induces pentraxin 3 expression in multiple acute lung injury models in rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292:L144–L153
Han B, Mura M, Andrade CF, Okutani D, Lodyga M, dos Santos CC, Keshavjee S, Matthay M, Liu M (2005) TNFalpha-induced long pentraxin PTX3 expression in human lung epithelial cells via JNK. J Immunol 175:8303–8311
Parrish WR, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ (2008) Experimental therapeutic strategies for severe sepsis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1144:210–236
Polli F, Savioli M, Cugno M, Taccone P, Bellani G, Spanu P, Pesenti A, Iapichino G, Gattinoni L (2009) Effects of recombinant human activated protein C on the fibrinolytic system of patients undergoing conventional or tight glycemic control. Minerva Anestesiol 75:1–10
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by a liberal grant for clinical research from Eli Lilly (F1K0020); by funding from the Italian Ministry for University and Scientific Research (MIUR, project FIRB and 2004060419); by the Italian Health Ministry; by the European Commission (Contract 2008-202156 “TOLERAGE”, LSHG-CT-2005-005203 “MUGEN”, LSHP-CT-2003-503240 “MUVAPRED”, SP5B-CT-2006-044161 “FLUINNATE”); by Telethon (grant no. GGP05095); and by the CARIPLO foundation (Project Nobel). We thank all patients who participated in this study and their families. We thank all the staff of our ICUs for their constant efforts to assure the best possible care to all our patients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Pesenti and A. Mantovani contributed equally to this work.
This article is discussed in the editorial available at: doi:10.1007/s00134-010-1758-z.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mauri, T., Bellani, G., Patroniti, N. et al. Persisting high levels of plasma pentraxin 3 over the first days after severe sepsis and septic shock onset are associated with mortality. Intensive Care Med 36, 621–629 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-010-1752-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-010-1752-5