Abstract
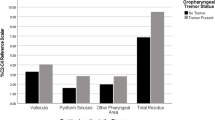
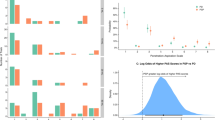
Parkinson’s disease is associated with both swallowing and respiratory dysfunction, increasing the risk of aspiration and pneumonia. Previous studies have shown improvements in measurements of swallowing and respiration with levodopa; however, the studies are small and some studies show conflicting reports. The aim of this study was to further investigate the effect of levodopa on respiration. Ten patients with Parkinson’s disease were tested “On” and “Off” levodopa. Assessments included Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), coordination of swallowing and respiration, timed-test of swallowing, lung function testing, and, qualitative assessment of swallowing. There was a nonsignificant trend to lower volume per swallow when “On” levodopa, significant reduction in lung function when “On” levodopa, but no difference in coordination of swallowing and respiration or qualitative assessment of swallowing. There was a significant increase in motor examination score of the UPDRS when “Off” levodopa compared to “On.” There may be a reduction in efficiency of swallowing with levodopa medication without any apparent increase in risk of aspiration. These pilot data suggest that further evaluation with larger numbers of participants is justified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkinson J. An Essay on the Shaking Palsy. London: Sherwood, Neely and Jones; 1817.
Morgante L, Salemi G, Meneghini F, Rosa DEA, Epifanio A, Grigoletto F, Ragonese P, Patti F, Reggio A, Perri DR, Savettieri G. Parkinson disease survival: a population-based study. Arch Neurol 2000;57:507–512.
Fall PA, Saleh A, Fredrickson M, Olsson JE, Granerus AK. Survival time, mortality, and cause of death in elderly patients with Parkinson’s disease: a 9-year follow-up. Mov Disord 2003;18:1312–1316.
Volonte MA, Porta M, Comi G. Clinical assessment of dysphagia in early phases of Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 2002;23 Suppl 2:S121–S122.
Johnston BT, Li Q, Castell JA, Castell DO. Swallowing and esophageal function in Parkinson’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol 1995;90:1741–1746.
Stroudley J, Walsh M. Radiological assessment of dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease. Br J Radiol 1991;64:890–893.
Edwards LL, Quigley EM, Pfeiffer RF. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: frequency and pathophysiology. Neurology 1992;42:726–732.
Nagaya M, Kachi T, Yamada T, Igata A. Videofluorographic study of swallowing in Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia 1998;13:95–100.
Pinnington LL, Muhiddin KA, Ellis RE, Playford ED. Non-invasive assessment of swallowing and respiration in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 2000;247:773–777.
Clarke CE, Gullaksen E, Macdonald S, Lowe F. Referral criteria for speech and language therapy assessment of dysphagia caused by idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 1998;97:27–35.
Ali GN, Wallace KL, Schwartz R, DeCarle DJ, Zagami AS, Cook IJ. Mechanisms of oral-pharyngeal dysphagia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Gastroenterology 1996;110:383–392.
Nilsson H, Ekberg O, Olsson R, Hindfelt B. Quantitative assessment of oral and pharyngeal function in Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia 1996;11:144–150.
Potulska A, Friedman A, Krolicki L, Spychala A. Swallowing disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2003;9:349–353.
Blumin JH, Pcolinsky DE, Atkins JP. Laryngeal findings in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2004;113:253–258.
Monte FS, da Silva-Junior FP, Braga-Neto P, Nobre e Souza MA, Sales de Bruin VM. Swallowing abnormalities and dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 2005;20:457–462.
Muller J, Wenning GK, Verny M, McKee A, Chaudhuri KR, Jellinger K, Poewe W, Litvan I. Progression of dysarthria and dysphagia in postmortem-confirmed parkinsonian disorders. Arch Neurol 2001;58:259–264.
Bushmann M, Dobmeyer SM, Leeker L, Perlmutter JS. Swallowing abnormalities and their response to treatment in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 1989;39:1309–1314.
Ding R, Logemann JA. Pneumonia in stroke patients: a retrospective study. Dysphagia 2000;15:51–57.
Langmore SE, Terpenning MS, Schork A, Chen Y, Murray JT, Lopatin D, Loesche WJ. Predictors of aspiration pneumonia: how important is dysphagia? Dysphagia 1998;13:69–81.
Shill H, Stacy M. Respiratory function in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurosci 1998;5:131–135.
Brown LK. Respiratory dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Chest Med 1994;15:715–727.
Sathyaprabha TN, Kapavarapu PK, Pall PK, Thennarasu K, Raju TR. Pulmonary functions in Parkinson’s disease. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 2005;47:251–257.
Hovestadt A, Bogaard JM, Meerwaldt JD, van der Meche FG, Stigt J. Pulmonary function in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1989;52:329–333.
Sabate M, Gonzalez I, Ruperez F, Rodriguez M. Obstructive and restrictive pulmonary dysfunctions in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 1996;138:114–119.
Herer B, Arnulf I, Housset B. Effects of levodopa on pulmonary function in Parkinson’s disease. Chest 2001;119:387–393.
Fuh JL, Lee RC, Wang SJ, Lin CH, Wang PN, Chiang JH, Liu HC. Swallowing difficulty in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 1997;99:106–112.
Hunter PC, Crameri J, Austin S, Woodward MC, Hughes AJ. Response of parkinsonian swallowing dysfunction to dopaminergic stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1997;63:579–583.
McHorney CA, Robbins J, Lomax K, Rosenbek JC, Chignell K, Kramer AE, Bricker DE. The SWAL-QOL and SWAL-CARE outcomes tool for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults: III. Documentation of reliability and validity. Dysphagia 2002;17:97–114.
Hughes TA, Wiles CM. Clinical measurement of swallowing in health and in neurogenic dysphagia. QJM 1996;89:109–116.
Miller MR, Crapo R, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Enright P, van der Grinten CP, Gustafsson P, Jensen R, Johnson DC, MacIntyre N, McKay R, Navajas D, Pedersen OF, Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Wanger J. General considerations for lung function testing. Eur Respir J 2005;26:153–161.
Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Brusasco V, Crapo RO, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, van der Grinten CP, Gustafsson P, Hankinson J, Jensen R, Johnson DC, MacIntyre N, McKay R, Miller MR, Navajas D, Pedersen OF, Wanger J. Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Eur Respir J 2005;26:948–968.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by funds from the McGee Fellowship, Christchurch School of Medicine & Health Sciences, University of Otago.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Work was performed at the Van der Veer Institute for Parkinson's and Brain Research, Christchurch, New Zealand.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, A., Leow, L., Huckabee, ML. et al. A Pilot Study of Respiration and Swallowing Integration in Parkinson’s Disease: “On” and “Off” Levodopa. Dysphagia 23, 76–81 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9100-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9100-9