Abstract
Purpose
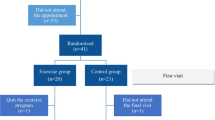
This study evaluated the efficacy of oropharyngeal exercises in children with symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA) after adenotonsillectomy.
Methods
Polysomnographic recordings were performed before adenotonsillectomy and 6 months after surgery. Patients with residual OSA (apnea-Hypopnea Index, AHI > 1 and persistence of respiratory symptoms) after adenotonsillectomy were randomized either to a group treated with oropharyngeal exercises (group 1) or to a control group (group 2). A morphofunctional evaluation with Glatzel and Rosenthal tests was performed before and after 2 months of exercises. All the subjects were re-evaluated after exercise through polysomnography and clinical evaluation. The improvement in OSA was defined by ΔAHI: (AHI at T1 − AHI at T2)/AHI at T1 × 100.
Results
Group 1 was composed of 14 subjects (mean age, 6.01 ± 1.55) while group 2 was composed of 13 subjects (mean age, 5.76 ± 0.82). The AHI was 16.79 ± 9.34 before adenotonsillectomy and 4.72 ± 3.04 after surgery (p < 0.001). The ΔAHI was significantly higher in group 1 (58.01 %; range from 40.51 to 75.51 %) than in group 2 (6.96 %; range from −23.04 to 36.96 %). Morphofunctional evaluation demonstrated a reduction in oral breathing (p = 0.002), positive Glatzel test (p < 0.05), positive Rosenthal test (p < 0.05), and increased labial seal (p < 0.001), and lip tone (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Oropharyngeal exercises may be considered as complementary therapy to adenotonsillectomy to effectively treat pediatric OSA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marcus CL, Brooks LJ, Draper KA, Gozal D, Halbower AC, Jones J, Schechter MS, Sheldon SH, Spruyt K, Ward SD, Lehmann C, Shiffman RN (2012) Clinical practice guideline. Diagnosis and Management of Childhood Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Pediatrics 130(3):576–584
Gozal D, Lipton AJ, Jones KL (2002) Circulating vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 25(1):59–65
Amin RS, Kimball TR, Bean JA, Jeffries JL, Willging JP, Cotton RT, Witt SA, Glascock BJ, Daniels SR (2002) Left ventricular hypertrophy and abnormal ventricular geometry in children and adolescents with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165(10):1395–1399
Kheirandish-Gozal L, Bhattacharjee R, Gozal D (2010) Autonomic alterations and endothelial dysfunction in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med 11(7):714–720
Chang SJ, Chae KY (2010) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children: epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and sequelae. Korean J Pediatr 53(10):863–871
Arens R, Marcus CL (2004) Pathophysiology of upper airway obstruction: a developmental perspective. Sleep 27(5):997–1019
Tauman R, Gozal D (2011) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children. Expert Rev Respir Med 5(3):425–440
Bhattacharjee R, Kheirandish-Gozal L, Spruyt K, Mitchell RB, Promchiarak J, Simakajornboon N, Kaditis AG, Splaingard D, Splaingard M, Brooks LJ, Marcus CL, Sin S, Arens R, Verhulst SL, Gozal D (2010) Adenotonsillectomy outcomes in treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in children: a multicenter retrospective study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182(5):676–683
Villa MP, Rizzoli A, Miano S, Malagola C (2011) Efficacy of rapid maxillary expansion in children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: 36 months of follow-up. Sleep Breath 15(2):179–184
Guimarães KC, Drager LF, Genta PR, Marcondes BF, Lorenzi-Filho G (2009) Effects of oropharyngeal exercises on patients with moderate obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179(10):962–966
Puhan MA, Suarez A, Cascio CL, Zahn A, Heitz M, Braendli O (2005) Didgeridoo playing as alternative treatment for obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 332(7536):266–270
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson A et al (2007) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated event: rules, terminology and technical specifications. Am Acad Sleep Med 1st ed Westchester
Marcus CL, Omlin KJ, Basinki DJ, Bailey SL, Rachal AB, Von Pechmann WS, Keens TG, Ward SL (1992) Normal polysomnographic values for children and adolescents. Am Rev Respir Dis 146(5 Pt1):1235–1239
Uliel S, Tauman R, Greenfeld M, Sivan Y (2004) Normal polysomnographic respiratory values in children and adolescents. Chest 125(3):872–878
Villa MP, Paolino MC, Castaldo R, Vanacore N, Rizzoli A, Miano S, Del Pozzo M, Montesano M (2013) Sleep clinical record: an aid to rapid and accurate diagnosis of pediatric sleep disordered breathing. Eur Respir J 41(6):1355–1361
Liistro G, Rombaux P, Belge C, Dury M, Aubert G, Rodenstein DO (2003) High Mallampati score and nasal obstruction are associated risk factors for obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 21(2):248–252
Friedman M, Ibrahim H, Joseph NJ (2004) Staging of obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome: a guide to appropriate treatment. Laryngoscope 114(3):454–459
Brouilette R, Hanson D, David R, Klemka L, Szatkowski A, Fernbach S, Hunt C (1984) A diagnostic approach to suspected obstructive sleep apnea in children. J Pediatr 105(1):10–14
DuPaul GJ, McGoey KE, Eckert TL, VanBrakle J (2001) Preschool children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: impairments in behavioral, social, and school functioning. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40(5):508–515
Chauvois A, Fournier M, Girardin F (1991) Rééducation des fonctions dans la thérapeutique orthodontique. Editions Sid, Vanves
Levrini A (1997) Terapia miofunzionale. Rieducazione neuromuscolare integrata. Masson S.p.A, Milan
Ye J, Liu H, Zhang GH, Li P, Yang QT, Liu X, Li Y (2010) Outcome of adenotonsillectomy for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 119(8):506–513
Kuhle S, Urschitz MS (2011) Anti-inflammatory medications for obstructive sleep apnea in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD007074
Kheirandish-Gozal L, Serpero LD, Dayyat E, Kim J, Goldman JL, Snow A, Bhattacharjee R, Gozal D (2009) Corticosteroids suppress in vitro tonsillar proliferation in children with obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 33(5):1077–1084
Goldbart AD, Goldman JL, Veling MC, Gozal D (2005) Leukotriene modifier therapy for adenotonsillar hypertrophy and sleep disordered breathing in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172(3):364–370
Kheirandish L, Goldbart AD, Gozal D (2006) Intranasal steroids and oral leukotriene modifier therapy in residual sleep disordered breathing following tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy in children. Pediatrics 117:E61–E66
Gozal D, Kheirandish-Gozal L (2008) The multiple challenges of obstructive sleep apnea in children: morbidity and treatment. Curr Opin Pediatr 20(6):654–658
Gallerano G, Ruoppolo G, Silvestri A (2012) Myofunctional and speech rehabilitation after orthodontic-surgical treatment of dento-maxillofacial dysgnathia. Prog Orthod 13(1):57–68
Guilleminault C, Huang YS, Monteyrol PJ, Sato R, Quo S, Lin CH (2013) Critical role of myofascial reeducation in pediatric sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Med 14(6):518–525
Fonteles CS, de Miranda Mota AC, Lima RA, Borges PC, da Silveira A (2013) Conservative management of severe open bite and feeding difficulties in patient with Noonan syndrome. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 50(2):242–248
Abeleira MT, Seoane-Romero JM, Outumuro M, Caamaño F, Suárez D, Carmona IT (2011) A multidisciplinary approach to the treatment of oral manifestations associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: a long-term case report. J Am Dent Assoc 142(12):1357–1364
Ethical standards
Informed consent was obtained from parents, and the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Sant’ Andrea Hospital.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villa, M.P., Brasili, L., Ferretti, A. et al. Oropharyngeal exercises to reduce symptoms of OSA after AT. Sleep Breath 19, 281–289 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1011-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1011-z