Abstract
Background
It is claimed that gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) increases in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). We aimed to evaluate the prevalence of GERD in patients with OSAS and primary snoring and identify OSAS-related risk factors associated with GERD.
Methods
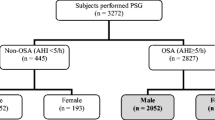
In this prospective, cross-sectional, multicenter study, in total 1,104 patients were recruited for polysomnography: 147 subjects were in non-OSAS (primary snoring) and 957 patients were in OSAS group. All patients completed a validated GERD questionnaire. Demographic, anthropometric characteristics, and medical history were recorded.
Results
The prevalence of GERD was similar in OSAS (38.9 %) and non-OSAS (32.0 %) groups (p = 0.064). There was no difference in terms of major gastroesophageal reflux (GER) symptoms (heartburn/acid regurgitation) between non-OSAS and mild, moderate, and severe OSAS groups. The prevalence of GERD was increased in female OSAS patients (46.6 %) compared to males (35.7 %) (p = 0.002). In OSAS patients with GERD, body mass index was greater (34.0 ± 7.0 vs. 33.1 ± 6.8, p = 0.049), waist (115.5 ± 13.9 vs. 113.1 ± 13.4, p = 0.007) and hip (117.9 ± 13.7 vs. 114.2 ± 12.8, p < 0.0001) circumferences were larger, and Epworth sleepiness scores were higher (10.3 ± 6.0 vs. 8.8 ± 5.6, p < 0.0001) than OSAS patients without GERD. Multivariate analysis showed that GERD was significantly associated with female gender, hip circumference, and daytime sleepiness.
Conclusions
In this large cohort, the prevalence of GERD was significantly increased in those with primary snoring and OSAS compared to the general population, but severity of OSAS did not influence GERD prevalence. The present results suggest that OSAS was not likely a causative factor but female gender, obesity, and sleepiness were related with prevalence of GERD in OSAS patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHI:
-
Apnea-hypopnea index
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- GER:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux
- GERD:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- NS:
-
Not significant
- OSAS:
-
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- REM:
-
Rapid eye movement
- SDB:
-
Sleep-disordered breathing
- SpO2 :
-
Pulse oximeter oxygen saturation
References
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S (1993) The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 328:1230–1235
Lam JC, Sharma SK, Lam B (2010) Obstructive sleep apnoea: definitions, epidemiology & natural history. Indian J Med Res 131:165–170
Kapur VK (2010) Obstructive sleep apnea: diagnosis, epidemiology, and economics. Respir Care 55:1155–1167
Schwartz AR, Patil SP, Laffan AM, Polotsky V, Schneider H, Smith PL (2008) Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5:185–192
Bradley TD, Floras JS (2009) Obstructive sleep apnoea and its cardiovascular consequences. Lancet 373:82–93
Selim B, Won C, Yaggi HK (2010) Cardiovascular consequences of sleep apnea. Clin Chest Med 31:203–220
Dong JY, Zhang YH, Qin LQ (2013) Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular risk: meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Atherosclerosis 229:489–495
Lam JCM, Lui MMS, Ip MSM (2010) Diabetes and metabolic aspects of OSA. Eur Respir Mon 50:189–215
Lévy P, Bonsignore MR, Eckel J (2009) Sleep, sleep-disordered breathing and metabolic consequences. Eur Respir J 34:243–260
Bor S, Mandiracioglu A, Kitapcioglu G, Caymaz-Bor C, Gilbert RJ (2005) Gastroesophageal reflux disease in a low income region in Turkey. Am J Gastroenterol 100:759–765
Hampel H, Abraham NS, El-Serag HB (2005) Meta-analysis: obesity and the risk for gastroesophageal reflux disease and its complications. Ann Intern Med 143:199–211
Cai N, Ji GZ, Fan ZN et al (2012) Association between body mass index and erosive esophagitis: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 18:2545–2553
Pasricha PJ (2003) Effect of sleep on gastroesophageal physiology and airway protective mechanisms. Am J Med 115(Suppl 3A):S114–S118
Foresman BH (2000) Sleep-related gastroesophageal reflux. J Am Osteopath Assoc 100 (12 Suppl Pt 2):S7–S10
Zanation AM, Senior BA (2005) The relationship between extraesophageal reflux (EER) and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Sleep Med Rev 9:453–458
Yang YX, Spencer G, Schutte-Rodin S, Brensinger C, Metz DC (2013) astroesophageal reflux and sleep events in obstructive sleep apnea. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:1017–1023
Morse CA, Quan SF, Mays MZ, Green C, Stephen G, Fass R (2004) Is there a relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and gastroesophageal reflux disease? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:761–768
Suzuki M, Saigusa H, Kurogi R, et al (2010) Arousals in obstructive sleep apnea patients with laryngopharyngeal and gastroesophageal reflux. Sleep Med 11:356–360
Valipour A, Makker HK, Hardy R, Emegbo S, Toma T, Spiro SG (2002) Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux in subjects with a breathing sleep disorder. Chest 121:1748–1753
Shepherd K, Hillman D, Holloway R, Eastwood P (2011) Mechanisms of nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux events in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 15:561–570
Demeter P, Pap A (2004) The relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and obstructive sleep apnea. J Gastroenterol 39:815–820
Kitapcioglu G, Mandiracioglu A, Bor S (2004) Psychometric and methodological characteristics of a culturally adjusted gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire. Dis Esophagus 17:228–234
Izci B, Ardic S, Firat H, Sahin A, Altinors M, Karacan I (2008) Reliability and validity studies of the Turkish version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breath 12:161–168
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson AL, Quan SF for the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2007) The AASM manual 2007 for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications. Westchester, Illinois: American Academy of Sleep Medicine
American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2005) International classification of sleep disorders, 2nd edition: Diagnostic and coding manual. Westchester, Illinois: American Academy of Sleep Medicine
American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force (1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. Sleep; 22: 667–689
Locke GR, Talley NJ, Fett SL, Zinmeister AR, Melton LJ (1997) Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: A population based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology 112:1448–1456
Bor S, Kitapcioglu G, Kasap E, Ilter T (2006) The prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in Turkey: lessons from a Helicobacter pylori prevalent country. J Clin Gastroenterol 40:S182
Bor S, Kitapcioglu G, Solak ZA, Ertilav M, Erdinc M (2010) The prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in patients with asthma and chronic obstrucive pulmonary disease. J Gastroent Hepatol 25:309–313
Shepherd KL, James AL, Musk AW, Hunter ML, Hillman DR, Eastwood PR (2011) Gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms are related to the presence and severity of obstructive sleep apnoea. J Sleep Res 20:241–249
Jung HK, Choung RS, Talley NJ (2010). Gastroesophageal reflux disease and sleep disorders: evidence for a causal link and therapeutic implications. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:22–29
Ju G, Yoon IY, Lee SD, Kim N (2013) Relationships between sleep disturbances and gastroesophageal reflux disease in Asian sleep clinic referrals. J Psychosom Res 75:551–555
Kim HN, Vorona RD, Winn MP, Doviak M, Johnson DA, Ware JC (2005) Symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and the severity of obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome are not related in sleep disorders center patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 21:1127–1133
Fass R, Quan SF, O'Connor GT, Ervin A, Iber C (2005) Predictors of heartburn during sleep in a large prospective cohort study. Chest 127:1658–1666
Green BT, Broughton WA, O'Connor JB (2003) Marked improvement in nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux in a large cohort of patients with obstructive sleep apnea treated with continuous positive airway pressure. Arch Intern Med 163:41–45
Conflict of interest
The manuscript entitled “Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and gastroesophageal reflux disease: the importance of obesity and gender” which we submit for consideration to be published in Sleep and Breathing is not under consideration for publication nor published elsewhere.
The investigation was performed at the Ege University Faculty of Medicine, Dr. Suat Seren Chest Diseases and Surgery Training and Research Hospital, and Katip Celebi University Faculty of Medicine. The work has been seen and approved by all coauthors. The authors have no proprietary, financial, professional, or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service, and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basoglu, O.K., Vardar, R., Tasbakan, M.S. et al. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and gastroesophageal reflux disease: the importance of obesity and gender. Sleep Breath 19, 585–592 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1051-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1051-4