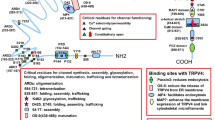
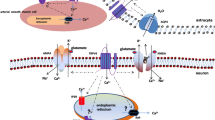
Abstract
Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4 (TRPV4) was originally described as a calcium-permeable nonselective cation channel. TRPV4 is now recognized as a polymodal ionotropic receptor: it is a broadly expressed, nonselective cation channel (permeable to calcium, potassium, magnesium, and sodium) that plays an important role in a multitude of physiological processes. TRPV4 is involved in maintaining homeostasis, serves as an osmosensor and thermosensor, can be activated directly by endogenous or exogenous chemical stimuli, and can be activated or sensitized indirectly via intracellular signaling pathways. Additionally, TRPV4 is upregulated in a variety of pathological conditions. In this review, we focus on the role of TRPV4 in mediating homeostasis and pathological events in the central nervous system (CNS). This review is composed of three parts. Section 1 describes the role of TRPV4 in maintaining homeostatic processes, including the volume of body water, ionic concentrations, volume, and the temperature. Section 2 describes the effects of activation and inhibition of TRPV4 in the CNS. Section 3 focuses on the role of TRPV4 during pathological events in CNS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Montell C, Rubin GM (1989) Molecular characterization of the Drosophila trp locus: a putative integral membrane protein required for phototransduction. Neuron 2(4):1313–1323
Cosens DJ, Manning A (1969) Abnormal electroretinogram from a Drosophila mutant. Nature 224(5216):285–287
Hardie RC, Minke B (1992) The trp gene is essential for a light-activated Ca2+ channel in Drosophila photoreceptors. Neuron 8(4):643–651
Damann N, Voets T, Nilius B (2008) TRPs in our senses. Curr Biol 18(18):R880–R889
Talavera K, Nilius B, Voets T (2008) Neuronal TRP channels: thermometers, pathfinders and life-savers. Trends Neurosci 31(6):287–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2008.03.002
Cai X (2008) Unicellular Ca2+ signaling 'toolkit' at the origin of metazoa. Mol Biol Evol 25(7):1357–1361. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msn077
Strotmann R, Harteneck C, Nunnenmacher K, Schultz G, Plant TD (2000) OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nat Cell Biol 2(10):695–702. https://doi.org/10.1038/35036318
Liedtke W, Choe Y, Marti-Renom MA, Bell AM, Denis CS, Sali A, Hudspeth AJ, Friedman JM et al (2000) Vanilloid receptor-related osmotically activated channel (VR-OAC), a candidate vertebrate osmoreceptor. Cell 103(3):525–535
Plant TD, Strotmann R (2007) Trpv4. Handb Exp Pharmacol (179):189–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-34891-7_11
Vennekens R, Owsianik G, Nilius B (2008) Vanilloid transient receptor potential cation channels: an overview. Curr Pharm Des 14(1):18–31
Vriens J, Owsianik G, Janssens A, Voets T, Nilius B (2007) Determinants of 4 alpha-phorbol sensitivity in transmembrane domains 3 and 4 of the cation channel TRPV4. J Biol Chem 282(17):12796–12803. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M610485200
Thorneloe KS, Sulpizio AC, Lin Z, Figueroa DJ, Clouse AK, McCafferty GP, Chendrimada TP, Lashinger ES et al (2008) N-((1S)-1-{[4-((2S)-2-{[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)sulfonyl]amino}-3-hydroxypropanoyl)-1 -piperazinyl]carbonyl}-3-methylbutyl)-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxamide (GSK1016790A), a novel and potent transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 channel agonist induces urinary bladder contraction and hyperactivity: Part I. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326(2):432–442. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.139295
Vriens J, Watanabe H, Janssens A, Droogmans G, Voets T, Nilius B (2004) Cell swelling, heat, and chemical agonists use distinct pathways for the activation of the cation channel TRPV4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(1):396–401. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0303329101
Wegierski T, Lewandrowski U, Muller B, Sickmann A, Walz G (2009) Tyrosine phosphorylation modulates the activity of TRPV4 in response to defined stimuli. J Biol Chem 284(5):2923–2933. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M805357200
Willette RN, Bao W, Nerurkar S, Yue TL, Doe CP, Stankus G, Turner GH, Ju H et al (2008) Systemic activation of the transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 4 channel causes endothelial failure and circulatory collapse: Part 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326(2):443–452. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.107.134551
Alessandri-Haber N, Dina OA, Joseph EK, Reichling D, Levine JD (2006) A transient receptor potential vanilloid 4-dependent mechanism of hyperalgesia is engaged by concerted action of inflammatory mediators. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 26(14):3864–3874. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5385-05.2006
Alessandri-Haber N, Dina OA, Yeh JJ, Parada CA, Reichling DB, Levine JD (2004) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 is essential in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain in the rat. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 24(18):4444–4452. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0242-04.2004
Grant AD, Cottrell GS, Amadesi S, Trevisani M, Nicoletti P, Materazzi S, Altier C, Cenac N et al (2007) Protease-activated receptor 2 sensitizes the transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 ion channel to cause mechanical hyperalgesia in mice. J Physiol 578(Pt 3):715–733. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2006.121111
Zhao P, Lieu T, Barlow N, Metcalf M, Veldhuis NA, Jensen DD, Kocan M, Sostegni S et al (2014) Cathepsin S causes inflammatory pain via biased agonism of PAR2 and TRPV4. J Biol Chem 289(39):27215–27234. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.599712
Tamura S, Morikawa Y, Senba E (2005) TRPV2, a capsaicin receptor homologue, is expressed predominantly in the neurotrophin-3-dependent subpopulation of primary sensory neurons. Neuroscience 130(1):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.09.021
Hjerling-Leffler J, Alqatari M, Ernfors P, Koltzenburg M (2007) Emergence of functional sensory subtypes as defined by transient receptor potential channel expression. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 27(10):2435–2443. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5614-06.2007
Ramsey IS, Delling M, Clapham DE (2006) An introduction to TRP channels. Annu Rev Physiol 68:619–647. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.68.040204.100431
Montell C, Birnbaumer L, Flockerzi V (2002) The TRP channels, a remarkably functional family. Cell 108(5):595–598
Watanabe H, Vriens J, Janssens A, Wondergem R, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2003) Modulation of TRPV4 gating by intra- and extracellular Ca2+. Cell Calcium 33(5–6):489–495
Verma P, Kumar A, Goswami C (2010) TRPV4-mediated channelopathies. Channels (Austin) 4(4):319–328
Becker D, Muller M, Leuner K, Jendrach M (2008) The C-terminal domain of TRPV4 is essential for plasma membrane localization. Mol Membr Biol 25(2):139–151. https://doi.org/10.1080/09687680701635237
Ramadass R, Becker D, Jendrach M, Bereiter-Hahn J (2007) Spectrally and spatially resolved fluorescence lifetime imaging in living cells: TRPV4-microfilament interactions. Arch Biochem Biophys 463(1):27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2007.01.036
Cuajungco MP, Grimm C, Oshima K, D'Hoedt D, Nilius B, Mensenkamp AR, Bindels RJ, Plomann M et al (2006) PACSINs bind to the TRPV4 cation channel. PACSIN 3 modulates the subcellular localization of TRPV4. J Biol Chem 281(27):18753–18762. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M602452200
D'hoedt D, Owsianik G, Prenen J, Cuajungco MP, Grimm C, Heller S, Voets T, Nilius B (2008) Stimulus-specific modulation of the cation channel TRPV4 by PACSIN 3. J Biol Chem 283(10):6272–6280
Suzuki M, Mizuno A, Kodaira K, Imai M (2003) Impaired pressure sensation in mice lacking TRPV4. J Biol Chem 278(25):22664–22668. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M302561200
Benfenati V, Caprini M, Dovizio M, Mylonakou MN, Ferroni S, Ottersen OP, Amiry-Moghaddam M (2011) An aquaporin-4/transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (AQP4/TRPV4) complex is essential for cell-volume control in astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(6):2563–2568. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1012867108
Liu X, Bandyopadhyay BC, Nakamoto T, Singh B, Liedtke W, Melvin JE, Ambudkar I (2006) A role for AQP5 in activation of TRPV4 by hypotonicity: concerted involvement of AQP5 and TRPV4 in regulation of cell volume recovery. J Biol Chem 281(22):15485–15495. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M600549200
Garcia-Elias A, Lorenzo IM, Vicente R, Valverde MA (2008) IP3 receptor binds to and sensitizes TRPV4 channel to osmotic stimuli via a calmodulin-binding site. J Biol Chem 283(46):31284–31288. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C800184200
Wang Y, Fu X, Gaiser S, Kottgen M, Kramer-Zucker A, Walz G, Wegierski T (2007) OS-9 regulates the transit and polyubiquitination of TRPV4 in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 282(50):36561–36570. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M703903200
Kottgen M, Buchholz B, Garcia-Gonzalez MA, Kotsis F, Fu X, Doerken M, Boehlke C, Steffl D et al (2008) TRPP2 and TRPV4 form a polymodal sensory channel complex. J Cell Biol 182(3):437–447. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200805124
Saliez J, Bouzin C, Rath G, Ghisdal P, Desjardins F, Rezzani R, Rodella LF, Vriens J et al (2008) Role of caveolar compartmentation in endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated relaxation: Ca2+ signals and gap junction function are regulated by caveolin in endothelial cells. Circulation 117(8):1065–1074. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.731679
Earley S, Heppner TJ, Nelson MT, Brayden JE (2005) TRPV4 forms a novel Ca2+ signaling complex with ryanodine receptors and BKCa channels. Circ Res 97(12):1270–1279. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000194321.60300.d6
Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Andrade YN, Arniges M, Fernandes J, Plata C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Vazquez E, Valverde MA (2008) Functional coupling of TRPV4 cationic channel and large conductance, calcium-dependent potassium channel in human bronchial epithelial cell lines. Pflugers Arch 457(1):149–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0516-3
Ding XL, Wang YH, Ning LP, Zhang Y, Ge HY, Jiang H, Wang R, Yue SW (2010) Involvement of TRPV4-NO-cGMP-PKG pathways in the development of thermal hyperalgesia following chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion in rats. Behav Brain Res 208(1):194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.11.034
Kohler R, Heyken WT, Heinau P, Schubert R, Si H, Kacik M, Busch C, Grgic I et al (2006) Evidence for a functional role of endothelial transient receptor potential V4 in shear stress-induced vasodilatation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26(7):1495–1502. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000225698.36212.6a
Bal-Price A, Moneer Z, Brown GC (2002) Nitric oxide induces rapid, calcium-dependent release of vesicular glutamate and ATP from cultured rat astrocytes. Glia 40(3):312–323. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.10124
Sonkusare SK, Dalsgaard T, Bonev AD, Hill-Eubanks DC, Kotlikoff MI, Scott JD, Santana LF, Nelson MT (2014) AKAP150-dependent cooperative TRPV4 channel gating is central to endothelium-dependent vasodilation and is disrupted in hypertension. Sci Signal 7(333):ra66
Cao DS, Yu SQ, Premkumar LS (2009) Modulation of transient receptor potential Vanilloid 4-mediated membrane currents and synaptic transmission by protein kinase C. Mol Pain 5:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-5-5
Alessandri-Haber N, Yeh JJ, Boyd AE, Parada CA, Chen X, Reichling DB, Levine JD (2003) Hypotonicity induces TRPV4-mediated nociception in rat. Neuron 39(3):497–511
Lee JC, Choe SY (2014) Age-related changes in the distribution of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 channel (TRPV4) in the central nervous system of rats. J Mol Histol 45(5):497–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-014-9578-z
Lee JC, Joo KM, Choe SY, Cha CI (2012) Region-specific changes in the immunoreactivity of TRPV4 expression in the central nervous system of SOD1(G93A) transgenic mice as an in vivo model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Mol Histol 43(6):625–631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9432-0
Dunn KM, Hill-Eubanks DC, Liedtke WB, Nelson MT (2013) TRPV4 channels stimulate Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in astrocytic endfeet and amplify neurovascular coupling responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(15):6157–6162. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1216514110
Benfenati V, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Caprini M, Mylonakou MN, Rapisarda C, Ottersen OP, Ferroni S (2007) Expression and functional characterization of transient receptor potential vanilloid-related channel 4 (TRPV4) in rat cortical astrocytes. Neuroscience 148(4):876–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.06.039
Shibasaki K, Ikenaka K, Tamalu F, Tominaga M, Ishizaki Y (2014) A novel subtype of astrocytes expressing TRPV4 (transient receptor potential vanilloid 4) regulates neuronal excitability via release of gliotransmitters. J Biol Chem 289(21):14470–14480. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.557132
Shibasaki K, Tominaga M (2007) Implication that TRPV4 activation induces the excitation of astrocytes. In: Proceedings of Annual Meeting of the Physiological Society of Japan Proceedings of Annual Meeting of the Physiological Society of Japan. PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY OF JAPAN, pp 082–082
Shi M, Du F, Liu Y, Li L, Cai J, Zhang GF, Xu XF, Lin T et al (2013) Glial cell-expressed mechanosensitive channel TRPV4 mediates infrasound-induced neuronal impairment. Acta Neuropathol 126(5):725–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1166-x
Liedtke W, Friedman JM (2003) Abnormal osmotic regulation in trpv4−/− mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(23):13698–13703. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1735416100
Simard M, Nedergaard M (2004) The neurobiology of glia in the context of water and ion homeostasis. Neuroscience 129(4):877–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.09.053
Koehler RC, Roman RJ, Harder DR (2009) Astrocytes and the regulation of cerebral blood flow. Trends Neurosci 32(3):160–169
Simard M, Arcuino G, Takano T, Liu QS, Nedergaard M (2003) Signaling at the gliovascular interface. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 23(27):9254–9262
Paulson OB, Newman EA (1987) Does the release of potassium from astrocyte endfeet regulate cerebral blood flow? Science 237(4817):896–898
Dunn KM, Bonev AD, Nelson MT (2011) Functional evidence of TRPV4-mediated Ca2+ signals in cortical astrocytes. FASEB J 25(1 Supplement):1024.1023–1024.1023
Dunn KM, Baylie RL, Nelson MT (2012) TRPV4 channels tune astrocytic endfoot Ca2+ to optimize neurovascular coupling. FASEB J 26(1 Supplement):685.610–685.610
Filosa JA, Bonev AD, Straub SV, Meredith AL, Wilkerson MK, Aldrich RW, Nelson MT (2006) Local potassium signaling couples neuronal activity to vasodilation in the brain. Nat Neurosci 9(11):1397–1403. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1779
Straub SV, Nelson MT (2007) Astrocytic calcium signaling: the information currency coupling neuronal activity to the cerebral microcirculation. Trends Cardiovasc Med 17(6):183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2007.05.001
Girouard H, Bonev AD, Hannah RM, Meredith A, Aldrich RW, Nelson MT (2010) Astrocytic endfoot Ca2+ and BK channels determine both arteriolar dilation and constriction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(8):3811–3816. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914722107
Strotmann R, Schultz G, Plant TD (2003) Ca2+-dependent potentiation of the nonselective cation channel TRPV4 is mediated by a C-terminal calmodulin binding site. J Biol Chem 278(29):26541–26549. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M302590200
Guler AD, Lee H, Iida T, Shimizu I, Tominaga M, Caterina M (2002) Heat-evoked activation of the ion channel, TRPV4. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 22 (15):6408-6414. doi:20026679
Abe J, Okazawa M, Adachi R, Matsumura K, Kobayashi S (2003) Primary cold-sensitive neurons in acutely dissociated cells of rat hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett 342(1–2):29–32
Travis KA, Bockholt HJ, Zardetto-Smith AM, Johnson AK (1995) In vitro thermosensitivity of the midline thalamus. Brain Res 686(1):17–22
Lowry CA, Lightman SL, Nutt DJ (2009) That warm fuzzy feeling: brain serotonergic neurons and the regulation of emotion. J Psychopharmacol 23(4):392–400. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881108099956
Güler AD, Lee H, Iida T, Shimizu I, Tominaga M, Caterina M (2002) Heat-evoked activation of the ion channel, TRPV4. J Neurosci 22(15):6408–6414
Chung M-K, Lee H, Caterina MJ (2003) Warm temperatures activate TRPV4 in mouse 308 keratinocytes. J Biol Chem 278(34):32037–32046
Shibasaki K, Sugio S, Takao K, Yamanaka A, Miyakawa T, Tominaga M, Ishizaki Y (2015) TRPV4 activation at the physiological temperature is a critical determinant of neuronal excitability and behavior. Pflügers Archiv-European. J Physiol 467(12):2495
Shibasaki K, Suzuki M, Mizuno A, Tominaga M (2007) Effects of body temperature on neural activity in the hippocampus: regulation of resting membrane potentials by transient receptor potential vanilloid 4. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 27(7):1566–1575. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4284-06.2007
Shibasaki K, Tominaga M, Ishizaki Y (2015) Hippocampal neuronal maturation triggers post-synaptic clustering of brain temperature-sensor TRPV4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 458(1):168–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.087
Lee H, Iida T, Mizuno A, Suzuki M, Caterina MJ (2005) Altered thermal selection behavior in mice lacking transient receptor potential vanilloid 4. J Neurosci 25(5):1304–1310
Todaka H, Taniguchi J, J-i S, Mizuno A, Suzuki M (2004) Warm temperature-sensitive transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) plays an essential role in thermal hyperalgesia. J Biol Chem 279(34):35133–35138
Yadav R, Jaryal AK, Mallick HN (2017) Participation of preoptic area TRPV4 ion channel in regulation of body temperature. J Therm Biol 66:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2017.04.001
Bicego KC, Scarpellini CS, Almeida MC, Gargaglioni LH (2016) Role of central TRPV4 in the activation of heat loss responses in WISTAR rats. FASEB J 30(1 Supplement):1243.1247–1243.1247
Vizin RCL, Scarpellini CS, Ishikawa DT, Correa GM, COd S, Gargaglioni L, Carrettiero DC, Bícego KC et al (2015) TRPV4 activates autonomic and behavioural warmth-defence responses in Wistar rats. Acta Physiol 214(2):275–289
Preston D, Simpson S, Danko C, Schroten H, Schwerk C, Blazer-Yost B (2017) TRPV4-mediated ion transport in the choroid plexus. FASEB J 31(1 Supplement):1007.1022–1007.1022
Danko C, Preston D, Simpson S, Blazer-Yost B (2017) Effects of a TRPV4 antagonist on hydrocephalus in Wpk rat model. FASEB J 31(1 Supplement):1042.1044–1042.1044
Ryskamp DA, Jo AO, Frye AM, Vazquez-Chona F, MacAulay N, Thoreson WB, Krizaj D (2014) Swelling and eicosanoid metabolites differentially gate TRPV4 channels in retinal neurons and glia. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 34(47):15689–15700. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2540-14.2014
Filosa JA, Yao X, Rath G (2013) TRPV4 and the regulation of vascular tone. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 61(2):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0b013e318279ba42
Watanabe H, Vriens J, Suh SH, Benham CD, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2002) Heat-evoked activation of TRPV4 channels in a HEK293 cell expression system and in native mouse aorta endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 277(49):47044–47051. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M208277200
Zhang DX, Mendoza SA, Bubolz AH, Mizuno A, Ge ZD, Li R, Warltier DC, Suzuki M et al (2009) Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4-deficient mice exhibit impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in vitro and in vivo. Hypertension 53(3):532–538. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.127100
Sullivan MN, Francis M, Pitts NL, Taylor MS, Earley S (2012) Optical recording reveals novel properties of GSK1016790A-induced vanilloid transient receptor potential channel TRPV4 activity in primary human endothelial cells. Mol Pharmacol 82(3):464–472. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.112.078584
Senadheera S, Bertrand PP, Grayson TH, Leader L, Murphy TV, Sandow SL (2013) Pregnancy-induced remodelling and enhanced endothelium-derived hyperpolarization-type vasodilator activity in rat uterine radial artery: transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4 channels, caveolae and myoendothelial gap junctions. J Anat 223(6):677–686. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.12127
Zhang L, Papadopoulos P, Hamel E (2013) Endothelial TRPV4 channels mediate dilation of cerebral arteries: impairment and recovery in cerebrovascular pathologies related to Alzheimer's disease. Br J Pharmacol 170(3):661–670. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12315
Bubolz AH, Mendoza SA, Zheng X, Zinkevich NS, Li R, Gutterman DD, Zhang DX (2012) Activation of endothelial TRPV4 channels mediates flow-induced dilation in human coronary arterioles: role of Ca2+ entry and mitochondrial ROS signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302(3):H634–H642. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00717.2011
Baratchi S, Almazi JG, Darby W, Tovar-Lopez FJ, Mitchell A, McIntyre P (2016) Shear stress mediates exocytosis of functional TRPV4 channels in endothelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(3):649–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2018-8
Sonkusare SK, Bonev AD, Ledoux J, Liedtke W, Kotlikoff MI, Heppner TJ, Hill-Eubanks DC, Nelson MT (2012) Elementary Ca2+ signals through endothelial TRPV4 channels regulate vascular function. Science 336(6081):597–601. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1216283
Campbell WB, Fleming I (2010) Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and endothelium-dependent responses. Pflügers Archiv European. J Physiol 459(6):881–895
Earley S, Pauyo T, Drapp R, Tavares MJ, Liedtke W, Brayden JE (2009) TRPV4-dependent dilation of peripheral resistance arteries influences arterial pressure. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys 297(3):H1096–H1102
Loot AE, Popp R, Fisslthaler B, Vriens J, Nilius B, Fleming I (2008) Role of cytochrome P450-dependent transient receptor potential V4 activation in flow-induced vasodilatation. Cardiovasc Res 80(3):445–452. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvn207
Vriens J, Owsianik G, Fisslthaler B, Suzuki M, Janssens A, Voets T, Morisseau C, Hammock BD et al (2005) Modulation of the Ca2 permeable cation channel TRPV4 by cytochrome P450 epoxygenases in vascular endothelium. Circ Res 97(9):908–915. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000187474.47805.30
Peixoto-Neves D, Wang Q, Leal-Cardoso JH, Rossoni LV, Jaggar JH (2015) Eugenol dilates mesenteric arteries and reduces systemic BP by activating endothelial cell TRPV4 channels. Br J Pharmacol 172(14):3484–3494. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13156
Sukumaran SV, Singh TU, Parida S, Reddy CEN, Thangamalai R, Kandasamy K, Singh V, Mishra SK (2013) TRPV4 channel activation leads to endothelium-dependent relaxation mediated by nitric oxide and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in rat pulmonary artery. Pharmacol Res 78:18–27
Adapala RK, Talasila PK, Bratz IN, Zhang DX, Suzuki M, Meszaros JG, Thodeti CK (2011) PKCalpha mediates acetylcholine-induced activation of TRPV4-dependent calcium influx in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301(3):H757–H765. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00142.2011
Saifeddine M, El-Daly M, Mihara K, Bunnett NW, McIntyre P, Altier C, Hollenberg MD, Ramachandran R (2015) GPCR-mediated EGF receptor transactivation regulates TRPV4 action in the vasculature. Br J Pharmacol 172(10):2493–2506. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13072
Butenko O, Dzamba D, Benesova J, Honsa P, Benfenati V, Rusnakova V, Ferroni S, Anderova M (2012) The increased activity of TRPV4 channel in the astrocytes of the adult rat hippocampus after cerebral hypoxia/ischemia. PLoS One 7(6):e39959. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039959
Jie P, Lu Z, Hong Z, Li L, Zhou L, Li Y, Zhou R, Zhou Y et al (2016) Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 is involved in neuronal injury in middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Mol Neurobiol 53(1):8–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8992-2
Jie P, Hong Z, Tian Y, Li Y, Lin L, Zhou L, Du Y, Chen L et al (2015) Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 induces apoptosis in hippocampus through downregulating PI3K/Akt and upregulating p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis 6:e1775. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.146
Bai JZ, Lipski J (2014) Involvement of TRPV4 channels in Abeta(40)-induced hippocampal cell death and astrocytic Ca(2+) signalling. Neurotoxicology 41:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2014.01.001
Ryskamp DA, Witkovsky P, Barabas P, Huang W, Koehler C, Akimov NP, Lee SH, Chauhan S et al (2011) The polymodal ion channel transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 modulates calcium flux, spiking rate, and apoptosis of mouse retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 31(19):7089–7101. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0359-11.2011
Taylor L, Arnér K, Ghosh F (2017) Specific inhibition of TRPV4 enhances retinal ganglion cell survival in adult porcine retinal explants. Exp Eye Res 154:10–21
Ye L, Kleiner S, Wu J, Sah R, Gupta RK, Banks AS, Cohen P, Khandekar MJ et al (2012) TRPV4 is a regulator of adipose oxidative metabolism, inflammation, and energy homeostasis. Cell 151(1):96–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.034
Klein CJ, Shi Y, Fecto F, Donaghy M, Nicholson G, McEntagart ME, Crosby AH, Wu Y et al (2011) TRPV4 mutations and cytotoxic hypercalcemia in axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathies. Neurology 76(10):887–894. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31820f2de3
Jang Y, Jung J, Kim H, Oh J, Jeon JH, Jung S, Kim KT, Cho H et al (2012) Axonal neuropathy-associated TRPV4 regulates neurotrophic factor-derived axonal growth. J Biol Chem 287(8):6014–6024. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.316315
Hunt RF, Hortopan GA, Gillespie A, Baraban SC (2012) A novel zebrafish model of hyperthermia-induced seizures reveals a role for TRPV4 channels and NMDA-type glutamate receptors. Exp Neurol 237(1):199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.06.013
Chen X, Sun FJ, Wei YJ, Wang LK, Zang ZL, Chen B, Li S, Liu SY et al (2016) Increased expression of transient receptor potential Vanilloid 4 in cortical lesions of patients with focal cortical dysplasia. CNS Neurosci Ther 22(4):280–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12494
Fecto F, Shi Y, Huda R, Martina M, Siddique T, Deng HX (2011) Mutant TRPV4-mediated toxicity is linked to increased constitutive function in axonal neuropathies. J Biol Chem 286(19):17281–17291. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.237685
Lu KT, Huang TC, Tsai YH, Yang YL (2017) Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4 channels mediate Na-K-Cl-co-transporter-induced brain edema after traumatic brain injury. J Neurochem 140(5):718–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13920
Alessandri-Haber N, Dina OA, Joseph EK, Reichling DB, Levine JD (2008) Interaction of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4, integrin, and SRC tyrosine kinase in mechanical hyperalgesia. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 28(5):1046–1057. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4497-07.2008
Zhang Y, Wang YH, Ge HY, Arendt-Nielsen L, Wang R, Yue SW (2008) A transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 contributes to mechanical allodynia following chronic compression of dorsal root ganglion in rats. Neurosci Lett 432(3):222–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2007.12.028
Zhao P, Lieu T, Barlow N, Sostegni S, Haerteis S, Korbmacher C, Liedtke W, Jimenez-Vargas NN et al (2015) Neutrophil elastase activates protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) and transient receptor potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) to cause inflammation and pain. J Biol Chem 290(22):13875–13887. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.642736
Walter BA, Purmessur D, Moon A, Occhiogrosso J, Laudier DM, Hecht AC, Iatridis JC (2016) Reduced tissue osmolarity increases TRPV4 expression and pro-inflammatory cytokines in intervertebral disc cells. Eur Cell Mater 32:123–136
Nayak PS, Wang Y, Najrana T, Priolo LM, Rios M, Shaw SK, Sanchez-Esteban J (2015) Mechanotransduction via TRPV4 regulates inflammation and differentiation in fetal mouse distal lung epithelial cells. Respir Res 16:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-015-0224-4
Dalsgaard T, Sonkusare SK, Teuscher C, Poynter ME, Nelson MT (2016) Pharmacological inhibitors of TRPV4 channels reduce cytokine production, restore endothelial function and increase survival in septic mice. Sci Rep 6:33841. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33841 https://www.nature.com/articles/srep33841#supplementary-information
Vergnolle N, Cenac N, Altier C, Cellars L, Chapman K, Zamponi G, Materazzi S, Nassini R et al (2010) A role for transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 in tonicity-induced neurogenic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 159(5):1161–1173
Scheraga RG, Abraham S, Niese KA, Southern BD, Grove LM, Hite RD, McDonald C, Hamilton TA et al (2016) TRPV4 mechanosensitive ion channel regulates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage phagocytosis. J Immunol 196(1):428–436. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1501688
Vergnolle N (2009) Protease-activated receptors as drug targets in inflammation and pain. Pharmacol Ther 123(3):292–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.05.004
Macfarlane SR, Seatter MJ, Kanke T, Hunter GD, Plevin R (2001) Proteinase-activated receptors. Pharmacol Rev 53(2):245–282
Poole DP, Amadesi S, Veldhuis NA, Abogadie FC, Lieu T, Darby W, Liedtke W, Lew MJ et al (2013) Protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) protein and transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) protein coupling is required for sustained inflammatory signaling. J Biol Chem 288(8):5790–5802. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.438184
Farber K, Kettenmann H (2005) Physiology of microglial cells. Brain research. Brain Res Rev 48(2):133–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.12.003
Inoue K, Nakajima K, Morimoto T, Kikuchi Y, Koizumi S, Illes P, Kohsaka S (1998) ATP stimulation of Ca2+-dependent plasminogen release from cultured microglia. Br J Pharmacol 123(7):1304–1310. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0701732
Kaushal V, Koeberle PD, Wang Y, Schlichter LC (2007) The Ca2+-activated K+ channel KCNN4/KCa3.1 contributes to microglia activation and nitric oxide-dependent neurodegeneration. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 27(1):234–244. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3593-06.2007
Fordyce CB, Jagasia R, Zhu X, Schlichter LC (2005) Microglia Kv1.3 channels contribute to their ability to kill neurons. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 25(31):7139–7149. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1251-05.2005
Alvarez DF, King JA, Weber D, Addison E, Liedtke W, Townsley MI (2006) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4-mediated disruption of the alveolar septal barrier: a novel mechanism of acute lung injury. Circ Res 99(9):988–995. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000247065.11756.19
Reiter B, Kraft R, Gunzel D, Zeissig S, Schulzke JD, Fromm M, Harteneck C (2006) TRPV4-mediated regulation of epithelial permeability. FASEB J: Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 20(11):1802–1812. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-5772com
Arniges M, Vazquez E, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Valverde MA (2004) Swelling-activated Ca2+ entry via TRPV4 channel is defective in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. J Biol Chem 279(52):54062–54068. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M409708200
Hamanaka K, Jian MY, Townsley MI, King JA, Liedtke W, Weber DS, Eyal FG, Clapp MM et al (2010) TRPV4 channels augment macrophage activation and ventilator-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 299(3):L353–L362. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00315.2009
Jie P, Tian Y, Hong Z, Li L, Zhou L, Chen L, Chen L (2015) Blockage of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 inhibits brain edema in middle cerebral artery occlusion mice. Front Cell Neurosci 9:141. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00141
Iuso A, Krizaj D (2016) TRPV4-AQP4 interactions 'turbocharge' astroglial sensitivity to small osmotic gradients. Channels (Austin) 10(3):172–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336950.2016.1140956
Balakrishna S, Song W, Achanta S, Doran SF, Liu B, Kaelberer MM, Yu Z, Sui A et al (2014) TRPV4 inhibition counteracts edema and inflammation and improves pulmonary function and oxygen saturation in chemically induced acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307(2):L158–L172. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00065.2014
Thorneloe KS, Cheung M, Bao W, Alsaid H, Lenhard S, Jian MY, Costell M, Maniscalco-Hauk K et al (2012) An orally active TRPV4 channel blocker prevents and resolves pulmonary edema induced by heart failure. Sci Transl Med 4(159):159ra148. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3004276
Hamanaka K, Jian M-Y, Weber DS, Alvarez DF, Townsley MI, Al-Mehdi AB, King JA, Liedtke W et al (2007) TRPV4 initiates the acute calcium-dependent permeability increase during ventilator-induced lung injury in isolated mouse lungs. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 293(4):L923–L932
Jian MY, King JA, Al-Mehdi AB, Liedtke W, Townsley MI (2008) High vascular pressure-induced lung injury requires P450 epoxygenase-dependent activation of TRPV4. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 38(4):386–392. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2007-0192OC
Matsumoto K, Utsumi D, Amagase K, Tominaga M, Kato S (2017) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) regulates vascular endothelial permeability during colonic inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis. FASEB J 31(1 Supplement):1049.1044–1049.1044
Narita K, Sasamoto S, Koizumi S, Okazaki S, Nakamura H, Inoue T, Takeda S (2015) TRPV4 regulates the integrity of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier and modulates transepithelial protein transport. FASEB J : Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 29(6):2247–2259. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.14-261396
O’Neil RG, Wu L, Brown RC (2006) TRPV4 channel expression and function in blood-brain barrier (BBB) microvessel endothelial cells. FASEB J 20(4):A329–A329
Lipski J, Park TI, Li D, Lee SC, Trevarton AJ, Chung KK, Freestone PS, Bai JZ (2006) Involvement of TRP-like channels in the acute ischemic response of hippocampal CA1 neurons in brain slices. Brain Res 1077(1):187–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2006.01.016
Li L, Qu W, Zhou L, Lu Z, Jie P, Chen L, Chen L (2013) Activation of transient receptor potential Vanilloid 4 increases NMDA-activated current in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Front Cell Neurosci 7:17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00017
Goldenberg NM, Ravindran K, Kuebler WM (2015) TRPV4: physiological role and therapeutic potential in respiratory diseases. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388(4):421–436
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (NRF-2015H1D3A1066543, NRF-2017R1C1B2011772) and the Korea Healthcare Technology Research & Development Project, Ministry for Health & Welfare Affairs, Republic of Korea (HR16C0002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, H., Lee, SH., Kim, KT. et al. TRPV4: a Sensor for Homeostasis and Pathological Events in the CNS. Mol Neurobiol 55, 8695–8708 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0998-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0998-8